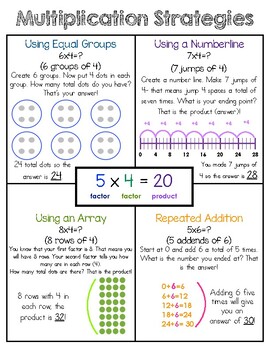
Multiplication and Division Strategies Anchor Chart
Explorations in Education
125 Followers
Grade Levels
2nd - 5th, Homeschool
Subjects
Resource Type
Standards
CCSS3.OA.A.1
CCSS3.OA.A.2
CCSS3.OA.A.3
CCSS3.OA.A.4
Formats Included
- PDF
Explorations in Education
125 Followers
What educators are saying
Thank you for the anchor chart that was readable and my students were able to put into their math spirals.
I love these! I printed them in poster size and hung them up so students could use them as a resource.
Description
This is an anchor chart that can be printed for students or enlarged on a poster maker. It goes through various strategies to solve both multiplication and division problems. It also includes vocabulary for each operation.
Total Pages
Answer Key
N/A
Teaching Duration
N/A
Report this resource to TPT
Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT’s content guidelines.
Standards
to see state-specific standards (only available in the US).
CCSS3.OA.A.1
Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as 5 × 7.
CCSS3.OA.A.2
Interpret whole-number quotients of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 56 ÷ 8 as the number of objects in each share when 56 objects are partitioned equally into 8 shares, or as a number of shares when 56 objects are partitioned into equal shares of 8 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a number of shares or a number of groups can be expressed as 56 ÷ 8.
CCSS3.OA.A.3
Use multiplication and division within 100 to solve word problems in situations involving equal groups, arrays, and measurement quantities, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem.
CCSS3.OA.A.4
Determine the unknown whole number in a multiplication or division equation relating three whole numbers. For example, determine the unknown number that makes the equation true in each of the equations 8 × ? = 48, 5 = __ ÷ 3, 6 × 6 = ?.